Pediatric
Schreiber’s Commitment to Children’s Healthcare
November 20, 2023World Children’s Day is a time to reflect on the challenges that children face and to highlight the initiatives that are making a positive impact on their lives. This year, we’d like to draw your attention to the critical issues surrounding children’s healthcare and the efforts we’re making here at the Schreiber Center for Pediatric Development to address these challenges.
Access Disparities
One of the most pressing issues in children’s healthcare is the glaring disparities in access to medical services. Many children in underprivileged communities continue to lack proper healthcare due to financial, geographical, and cultural barriers. We recognize this inequality and have made great strides to help bridge this gap in central Pennsylvania.

We provide comprehensive pediatric care services and affordable healthcare options. As one of the only pediatric therapy centers in the area to accept Medicaid insurance as a payment option we service many children who otherwise would not receive the pediatric therapy services they need. Our ‘Kids’ Care Fund’ ensures that every child that comes to our center for therapy receives the care they need, regardless of their family’s financial situation.
Childhood Disabilities
Children with disabilities require specialized care and support to thrive and reach their full potential. One size does not fit all when it comes to healthcare for children. Which is why we offer a range of therapy services, including mental and behavioral health, physical, occupational, and speech therapy, each tailored to the unique needs of the individual child.

Through these programs, our Schreiber kids are provided with the tools they need to overcome the challenges they face, enabling them to flourish in their own way.
Pediatric Mental Health
The increasing mental health challenges in children are a mounting concern for parents, with far-reaching implications for the community. To help address this issue, we have integrated a new mental and behavioral health therapy department into our holistic approach to pediatric care that focuses on play-based and cognitive-behavioral therapies.

Our pediatric therapists specialize in diagnoses such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, autism spectrum disorders, depression, stress, anxiety, trauma related disorders, adoption, divorce, abuse, grief, and more. By providing counseling, emotional support, and resources, it is our goal to contribute to the emotional well-being of both children and their families and is an essential part of our commitment to the overall health and happiness of the children we serve.
Inclusive Education for Kids
The link between education and health is undeniable, yet many children face health issues that hinder their ability to access quality education, creating a cycle of disadvantage. Our S.T.A.R.S. Preschool is dedicated to reverse mainstreaming and has expanded our program that was once exclusively designed for children with special needs to include children of all abilities.
It is our hope that by playing together, our kiddos learn to not only understand and accept diversity, but to also value it. We also collaborate with the IU13 program to ensure that children with disabilities have equal access to quality education and are receiving any additional help they need. It is important to us that every child has the opportunity to learn and grow, regardless of their physical or mental challenges.
Support for Special Needs Children
We are proud to serve children with special needs and ensure that they receive the care and attention they require to thrive. We never hesitate to go the extra mile in providing resources and support for children with complex medical needs and chronic conditions. This includes assistance with obtaining medical equipment, specialized care, and respite services. We believe that by providing these services and support to our Schreiber families, children with special needs can lead fulfilling lives, and their families can find solace in knowing that their child’s unique requirements are met with compassion and expertise.

On World Children’s Day, we strive to be a beacon of hope and support, addressing the multifaceted challenges that children’s healthcare faces. Through our commitment to accessible, compassionate, and comprehensive care, we are working to improve the lives of children and their families, helping them overcome obstacles and reach their full potential. When every child receives the healthcare, support, and opportunities they deserve our purpose will be fulfilled.
To help us continue to provide necessary therapies to our Schreiber kids, consider donating to our Kids’ Care Fund to support our uncompensated care costs.
As a nationally recognized pediatric facility, the Schreiber Center for Pediatric Development provides family-centered education and therapy programs for infants, children and adolescents with disabilities, developmental delays, and acquired injuries. Our goal-oriented approach maximizes each child’s ability to function independently within the community.
ExtraGive Funds Pediatric Therapy at Schreiber
October 31, 2023Every child deserves the opportunity to lead a healthy and fulfilling life. At the Schreiber Center for Pediatric Development, we are committed to ensuring that every child, regardless of their abilities or financial circumstances, has access to the quality care they need.
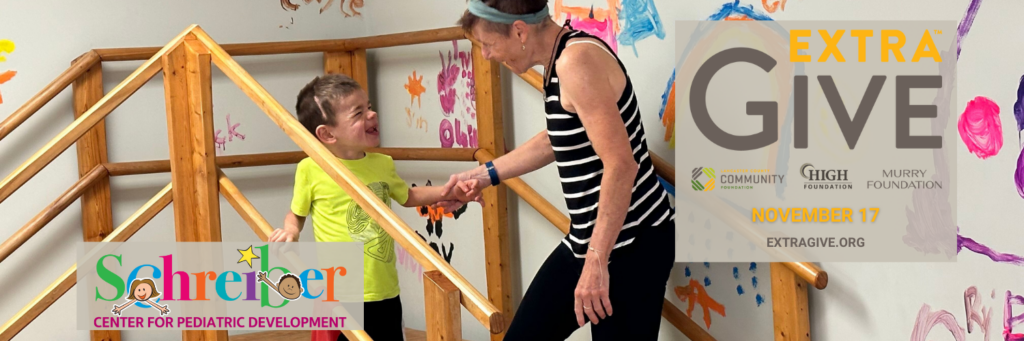
The ExtraGive event (https://www.extragive.org/) is a remarkable opportunity for us to come together as a community and make a significant impact on the lives of children who rely on our pediatric therapy programs. Your generous donations during the ExtraGive event will directly benefit our occupational, physical, speech, and mental and behavioral health therapy programs, as well as our “Kids’ Care Fund” designed to cover uncompensated care expenses.
Pediatric Occupational Therapy: Feeding Program
Pediatric occupational therapy is a crucial component of the services we provide at Schreiber Center for Pediatric Development. Many children face challenges related to feeding and nutrition, and our goal is to support them in developing the necessary skills for a healthy diet. Your donations will help us establish a new feeding program that will provide personalized support to children with various feeding difficulties.

Feeding issues can be a source of tremendous stress for families, and your contributions will make it possible for us to offer specialized therapy, equipment, and resources to help these children develop the skills they need to thrive.
Pediatric Physical Therapy: Medical Mobility Equipment

Children with mobility impairments often require specialized equipment to enhance their mobility and independence. The funds donated during the ExtraGive event will be instrumental in acquiring essential medical mobility equipment for our pediatric physical therapy program.
These devices can be life-changing for children, enabling them to participate in everyday activities and improving their overall quality of life. Your support will help us ensure that no child in central PA is left without the necessary equipment to navigate the world around them.
Pediatric Speech Therapy: Communication Devices
Communication is a fundamental aspect of a child’s development, and for some children, it can be particularly challenging. Our pediatric speech therapy program is dedicated to helping children develop their communication skills, and your donations will play a pivotal role in achieving this goal.
We aim to provide augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices, speech-generating devices (SGDs), and other assistive communication tools to children who need them. These devices empower children to express themselves, connect with others, and engage with the world in meaningful ways.

Mental and Behavioral Health Therapy: After-School Social Programs
At Schreiber Center for Pediatric Development, we recognize the importance of mental and behavioral health in a child’s overall well-being. Your donations will support our after-school social programs, including the popular “After-School Lego Club,” designed specifically for children with autism.

These programs offer a safe and supportive environment where children can develop social skills, build friendships, and gain confidence. Your contributions will enable us to expand these programs, reaching even more children who can benefit from them.
The “Kids’ Care Fund”: Ensuring Access to Care for All
In addition to directly supporting our therapy programs, your generous donations during the ExtraGive event will be added to our “Kids’ Care Fund.” This fund serves as a safety net, ensuring that all disabled children receive the care they need, regardless of their families’ financial circumstances.
The “Kids’ Care Fund” is a savings account that bridges the gap between what private insurance and Medicaid supplements cover and the actual cost of care. At Schreiber Pediatric, we have always made the promise that no child will be turned away, and your contributions help us fulfill this commitment.

Your support during the ExtraGive event will have a profound and lasting impact on the lives of the children we serve through our pediatric therapy programs at Schreiber Center for Pediatric Development. Whether it’s helping a child improve their feeding skills, providing essential mobility equipment, enabling communication, or fostering social connections, your generosity makes it all possible.
Furthermore, your donations will contribute to the “Kids’ Care Fund,” ensuring that no child is denied the care they deserve due to financial constraints. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of Schreiber kids and their families, offering hope, support, and a brighter future. Join us in transforming lives and creating a more inclusive and compassionate community for all children in central PA. Donate during the ExtraGive event and be a part of something truly extraordinary.
Down Syndrome Awareness Month
October 16, 2023This month we have the opportunity to raise public awareness about the condition Down Syndrome, as we advocate for the inclusion and acceptance of people with Down Syndrome. It is an unfortunate fact that people with Down Syndrome continue to face stereotypes and misconceptions about their abilities. We urge you to take this month to learn more about this condition and help us to spread the message of acceptance and respect for all people with Down Syndrome all year round.
What is Down Syndrome?
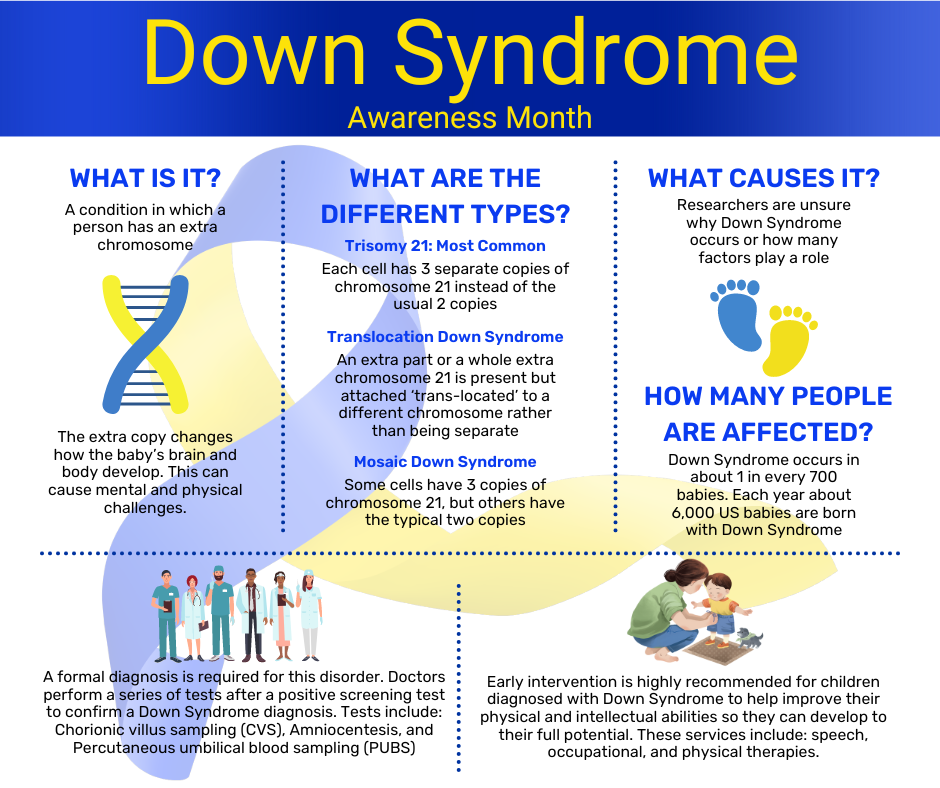
Down Syndrome is a genetic condition that occurs when a person is born with an extra chromosome. People are typically born with 46 chromosomes, but a person with Down Syndrome has an extra copy or part of an extra copy or chromosome 21.
There are three different types of Down Syndrome, and they are all dependent on how the extra chromosome 21 presents within the diagnosed person.
The most common type of Down Syndrome is called Trisomy 21, and about 95% of people who are diagnosed with Down Syndrome are diagnosed with this type. Trisomy 21 means that each cell within the body has three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual two copies.
The second most common type of Down Syndrome is called Translocation Down Syndrome and only about 3% of people diagnosed with Down Syndrome have this type. Translocation Down Syndrome occurs when an extra part or a whole extra chromosome 21 is present but attached ‘trans-located’ to a different chromosome, rather than being separate as is the case of Trisomy 21.
The least common type of Down Syndrome is called Mosaic Down Syndrome and only 2% of people who are diagnosed with Down Syndrome have this type. Mosaic Down Syndrome means that some of the cells in the body have three copies of chromosome 21, but other cells in the body still only have the typical two copies. Because only some of the cells in the body contain this additional chromosome this type of Down Syndrome presents less dominantly in physical features than the other two.
How do I know if my child has Down Syndrome?
About 6,000 babies are born with Down Syndrome in the US every year: that’s about 1 in every 700 babies. Down Syndrome can be detected in utero with screening tests and/or diagnostic tests. Screening tests can tell you if your pregnancy has a higher or lower chance of resulting in a baby with Down Syndrome, but they do not provide an absolute diagnosis. Diagnostic tests on the other hand, can typically detect whether a baby will have Down Syndrome. Diagnostic tests can be risky and are not generally performed until after a positive screening test. They include Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) which examines the material from the placenta, Amniocentesis which examines the amniotic fluid, and Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS) which examines the blood from the umbilical cord. Each of these tests look for changes in the chromosomes that would indicate a Down Syndrome diagnosis.
What causes Down Syndrome?
Researchers know that Down Syndrome occurs when a person is born with an extra chromosome 21, but they are unsure how or why the extra chromosome forms. Many researchers believe that there are several different factors that play a role in whether the extra chromosome 21 will form in utero, but they are not entirely sure what those factors are. It is known that the likelihood of a baby being born with Down Syndrome increases with a mother’s age, but because more women give birth before they turn 35, more babies with Down Syndrome are born to women under 35 years of age. Nothing that a parent does during pregnancy is known to cause Down Syndrome.
What are the complications of Down Syndrome?
About half of people with Down Syndrome also have a congenital heart defect. They are also more prone to hearing loss, ear infections, obstructive sleep apnea, respiratory issues, eye diseases, poor eyesight, Alzhemer’s disease, leukemia, thyroid disorders and intestinal blockages at birth that require surgery.
In addition to the physical complications that can come along with Down Syndrome, it can also cause intellectual and developmental symptoms that can lead to cognitive impairment. Similar to the physical complications these symptoms can range from mild to moderate and include short attention span, poor judgement, impulsive behavior, slow learning, and delayed language and speech development.
What is the treatment for Down Syndrome?
Making sure that a child with Down Syndrome receives services early in life will help them to improve their physical and intellectual abilities and ensure that they reach their full potential into adulthood. Most of the services recommended for children with Down Syndrome focus specifically on helping them minimize the effects of any intellectual or developmental symptoms the condition is responsible for. Early intervention services include speech therapy, occupational therapy, and physical therapy.
These therapies can be beneficial to children with Down Syndrome past the years of early intervention as well. Each person with Down Syndrome has different talents, and they all have the ability to thrive. Down Syndrome is a lifelong condition and children with Down Syndrome may need extra help or attention in school, but with the proper treatment plan and early intervention many people with Down Syndrome are able to be mainstreamed and attend regular classes with their peers.
If you child has been diagnosed with Down Syndrome and you are interested in learning more about how Schreiber’s Pediatric Therapies can help your child visit: http://www.schreiberpediatric.org/therapy-services/
As a nationally recognized pediatric facility, the Schreiber Center for Pediatric Development provides family-centered education and therapy programs for infants, children and adolescents with disabilities, developmental delays, and acquired injuries. Our goal-oriented approach maximizes each child’s ability to function independently within the community.
20 Tips for a Sensory Processing Disorder Friendly Halloween
October 12, 2023Halloween, with its costumes, candies, and eerie decorations, is a thrilling time for many children. However, for those with Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD), this holiday can present unique challenges. SPD can make the sensory overload of Halloween overwhelming. But fear not! In this blog post, we’ll share some invaluable sensory Halloween tips and ideas to ensure your child has a comfortable and enjoyable Halloween experience.
1. Prepare Your Child:
Start by preparing your child for Halloween. Explain the concept of the holiday and what to expect. Videos can be a great tool to help them visualize what Halloween is all about.
2. Visual Calendar:
Create a visual calendar to help your child countdown to Halloween. Seeing the days pass can provide a sense of predictability and reduce anxiety.
3. Pumpkin Alternatives:
Many children with SPD don’t enjoy carving pumpkins. Encourage them to paint or draw on them instead.
4. Comfortable Costumes:
Choose costumes that are comfortable and not overly frightening. Let your child have a say in picking their costume to ensure it aligns with their sensory preferences.
5. Less Is Best:
Remember, when it comes to costumes, less is often best. Avoid bulky or restrictive outfits that can cause discomfort.
6. Familiar Clothing:
Consider creating costumes from familiar clothing items. This can help your child feel more at ease in their costume.

7. Gradual Costume Familiarization:
Practice wearing the costume for short intervals, starting with just a few minutes and gradually working up to longer periods.
8. Show Costume Varieties:
Show your child pictures of different costumes they may encounter while trick-or-treating. Familiarity can ease anxiety.
9. Avoid Masks:
Most children with SPD don’t like masks. Opt for face paint or makeup instead, which can be less restrictive. Costumes that don’t need a mask, face paint, or makeup may be the best option for some children.
10. Walk the Route:
Before Halloween night, walk the trick-or-treat route a few times with your child to make it familiar and less intimidating.
11. The Joy of Giving:
Remind your child that Halloween isn’t just about receiving treats. Encourage them to be the one who hands out candies to neighbors, which can be a rewarding experience.
12. Early Trick-or-Treating:
Consider going trick-or-treating earlier in the evening, before it gets dark and potentially spookier.
13. Bring a Friend:
Having a friend along can provide extra support and companionship for your child.

14. Respect Their Limits:
If your child becomes tired or no longer wants to participate, don’t push them to continue. Respect their limits and end the evening.
15. Avoid Crowds:
Try to avoid crowded areas and houses while trick-or-treating to reduce sensory overload.
16. Sensory Gear:
Bring noise reduction headphones and sunglasses if your child is sensitive to loud noises or bright lights.
17. Maintain Routine:
Stick to your child’s regular bedtime routine to provide a sense of stability on Halloween night.
18. Sensory Diet:
Complete a sensory diet before and after trick-or-treating, incorporating activities like brushing, joint compressions, heavy work, swinging, or trampolining.
19. Fine Motor Skills:
Have your child attempt to open candy wrappers themselves, which can help improve fine motor skills.

20. It’s Okay Not to Go Out:
Lastly, remember that if your child doesn’t want to go out for Halloween, that’s perfectly okay. Their comfort and well-being should always come first.
Halloween can be a magical time for children, and with these sensory Halloween tips and ideas, you can help your child with SPD enjoy the festivities while minimizing stress and sensory challenges. By being understanding, patient, and supportive, you can create a Halloween experience tailored to your child’s unique needs and preferences.
If you child has been diagnosed with Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy and you are interested in learning more about how Schreiber’s Pediatric Therapies can help your child visit: http://www.schreiberpediatric.org/therapy-services/
As a nationally recognized pediatric facility, the Schreiber Center for Pediatric Development provides family-centered education and therapy programs for infants, children and adolescents with disabilities, developmental delays, and acquired injuries. Our goal-oriented approach maximizes each child’s ability to function independently within the community.
Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy
September 29, 2023What is Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy?
Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy is a group of muscular dystrophies which can be inherited in various ways. It equally effects males and females and symptoms begin between 8 and 15 years of age. About 2 to 10 out of 100,000 people are affected by this muscle disorder which leads to muscle weakness and muscle wasting of varying severity. Most commonly the shoulder and pelvis muscles are affected and as it progresses the hips, shoulders, arms, legs, and back muscles all weaken. The symptoms are known to progress slowly and while there is no cure the life expectancy of an individual with this diagnosis is generally within a normal range since the heart and breathing muscles are not affected.
How do I know if my child has Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy?
The signs and symptoms of people with Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy can vary widely. Even among individuals within the same family there is a good chance that the signs and symptoms will not be the same. Since symptoms can begin at any age, it’s important to keep an eye out for these common signs throughout your child’s life:
- Inability to rise from a squatting position without using the arms for leverage
- Toe walking or walking on the balls of their feet
- A waddling gait when walking
- Difficulty running
- Joint stiffness
- Abnormal spine curvature (lordosis/scoliosis)
Because these signs and symptoms are common in other muscular dystrophies, it is critical to see a medical doctor and receive a formal diagnosis so that proper treatment can be obtained. The formal diagnosis is based on symptoms, symptom severity, age at which the symptoms began, and family medical history. Doctors will perform a series of tests including: electrodiagnostic tests, laboratory tests, muscle biopsies, imaging studies, electrocardiograms, and genetic testing to confirm their diagnosis.
What Causes Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy?
Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy is a neuromuscular genetic disorder that occurs when a faulty gene results in abnormal muscle function. Many genes have been identified as contributing to this disorder so while it can be passed from parent to child, the child also could be the first in the family to have muscular dystrophy.
What are the complications of Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy?
While it is rare for Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy to affect the heart, lungs, digestive system, or other body systems outside of the muscles, it is possible. Any time the heart or lungs are affected by muscular disorders there is a chance that life expectancy will be negatively affected.
What is the treatment of Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy?
While there is no cure for Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy there are treatments for it. Treatments range from medications that are prescribed by medical professionals to help relieve symptoms relating to Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy to physical, respiratory, occupational, and behavioral therapies to help reduce the process of muscle weakness and wasting. Treatment is individualized for each patient and designed to enhance quality of life.
If you child has been diagnosed with Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy and you are interested in learning more about how Schreiber’s Pediatric Therapies can help your child visit: http://www.schreiberpediatric.org/therapy-services/
As a nationally recognized pediatric facility, the Schreiber Center for Pediatric Development provides family-centered education and therapy programs for infants, children and adolescents with disabilities, developmental delays, and acquired injuries. Our goal-oriented approach maximizes each child’s ability to function independently within the community.
Anxiety in Kids
September 27, 2023What is Anxiety?
Anxiety is a NORMAL worry or uneasy feeling that causes kids to feel nervous and afraid. It can generate real and uncomfortable physical responses. Anxiety is often triggered by new situations which makes it very common in children. For some children, anxiety affects their behavior and thoughts daily, which can interfere with their home life, school, and their social well-being. For these children, professional help is often the best answer.
Use these tips to help you spot anxiety in your child and help them to learn skills to cope with their anxiety now and in the future.
How Anxiety Feels to Kids
Anxiety can be a confusing and scary feeling for kids, especially if they have never experienced these emotions and physiological effects before and don’t have a name for the way they are feeling. Even once a child knows that they have anxiety and the signs and symptoms they may experience when they become anxious, they may feel embarrassed or ashamed. The physical and psychological symptoms of anxiety can present in a variety of different ways in your child. Look for these common signs.

How Anxiety Shows Up in Kids
If your child is experiencing anxiety, they may begin to act differently. For some kids this may mean that they are acting out and becoming more difficult and defiant, but for other children it might mean that they begin to withdraw from social situations or even their families. It is important to remember that when it comes to anxiety in kids it is not a one size fits all situation. You know your child’s normal behavior better than anyone else, and the best person to determine if their behavior has suddenly or drastically changed. These are a few common signs that are associated with anxiety in kids.
Common Anxiety Triggers for Kids
Since anxiety is often triggered by new situations your child may experience a bout of anxiety occasionally, when something in their life feels different or beyond their control. There are several common triggers for anxiety in kids which range from social factors, or pressure to perform well, to fear of change or the future, and even conflict or change at home. Your child may be experiencing anxiety due to a variety of different things. Below are just a few examples of common anxiety triggers for kids.

Teach Your Child What They Can & Cannot Control
It can be very helpful to remind your child which things they are feeling anxious about are within their control, and which are not. You may find that much of what your child is anxious about are things they can’t control. So it’s important to teach them the difference between what they can and cannot control, so that they have a better understanding of their own anxieties. It can be helpful for kids with anxiety to have a list that they can refer to that explains these different behaviors. You can use the list below as a starting point and tailor it to your child’s specific anxiety triggers for a helpful guide they can refer to as often as they may need.

Grounding Techniques for Kids
The 5-4-3-2-1 Grounding technique is helpful both for adults and kids with anxiety as it helps connect the anxious party with the present by exploring the five senses and their immediate surroundings. This technique is especially helpful if the cause of their anxiety is something that already happened or may happen in the future. If the child is currently in the midst of their anxiety trigger the grounding technique may be a bit difficult for them to accomplish, but is still worth an attempt as long as it can be practiced safely. When your child is feeling anxious encourage them to complete the following grounding exercise and see if it helps bring them back to a point of relative calmness. The convenience of being able to perform this technique in almost any location is just one of the many reasons it is so beneficial to learn and remember.

While all children are likely to experience some anxiety in their life on occasion, it is important to recognize if your child’s anxiety has become severe enough to impact their daily lives. If this is the case seeing a pediatric behavioral health therapist may be in your child’s best interest as they can provide more individualistic approaches to help mitigate the causes and symptoms that your child is experiencing. They will also be able to help you and your child understand where the anxiety is coming from and tips, tricks, and tools to help reduce the anxiety your child feels.
If you are interested in learning more about how Schreiber’s Pediatric Behavioral Health Services can help your child visit http://www.schreiberpediatric.org/behavioral-health/
As a nationally recognized pediatric facility, the Schreiber Center for Pediatric Development provides family-centered education and therapy programs for infants, children and adolescents with disabilities, developmental delays, and acquired injuries. Our goal-oriented approach maximizes each child’s ability to function independently within the community.
Sam Leon-Durkee: Young man with a plan
April 19, 2022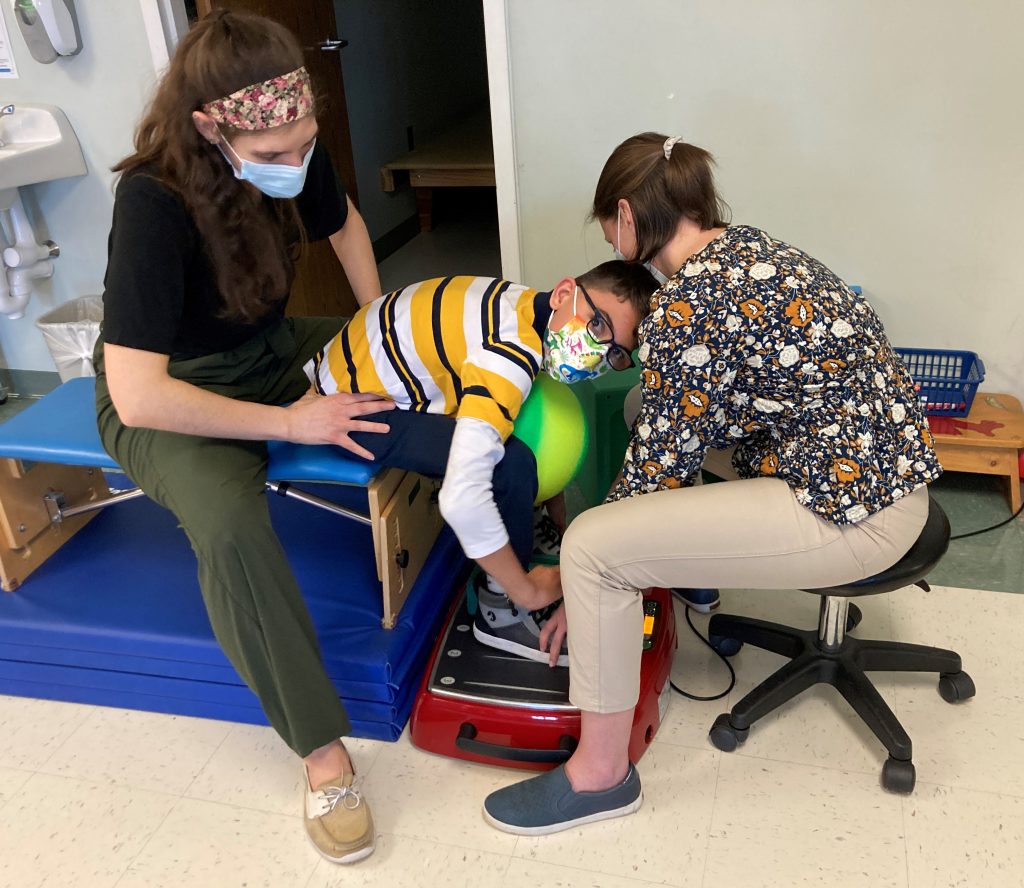
Sam Leon-Durkee started a recent physical therapy session working on a piece of equipment called a Galieleo vibration plate. He sat down on a bench, put his feet on the plate and, with the help of his physical therapist, Rachel Saufley, worked on standing up.
Sam was diagnosed with cerebral palsy at 18 months. He’s 12 now, and does a lot of work to increase his flexibility and mobility. The vibration plate helps reduce the muscle spasticity, or tightness, associated with CP so he can have a more effective therapy session.
Schreiber acquired the vibration plate in December thanks to a grant from the Gamber Foundation. Rachel said she uses it with Sam to help stretch his hamstrings. Sam put it a little differently.
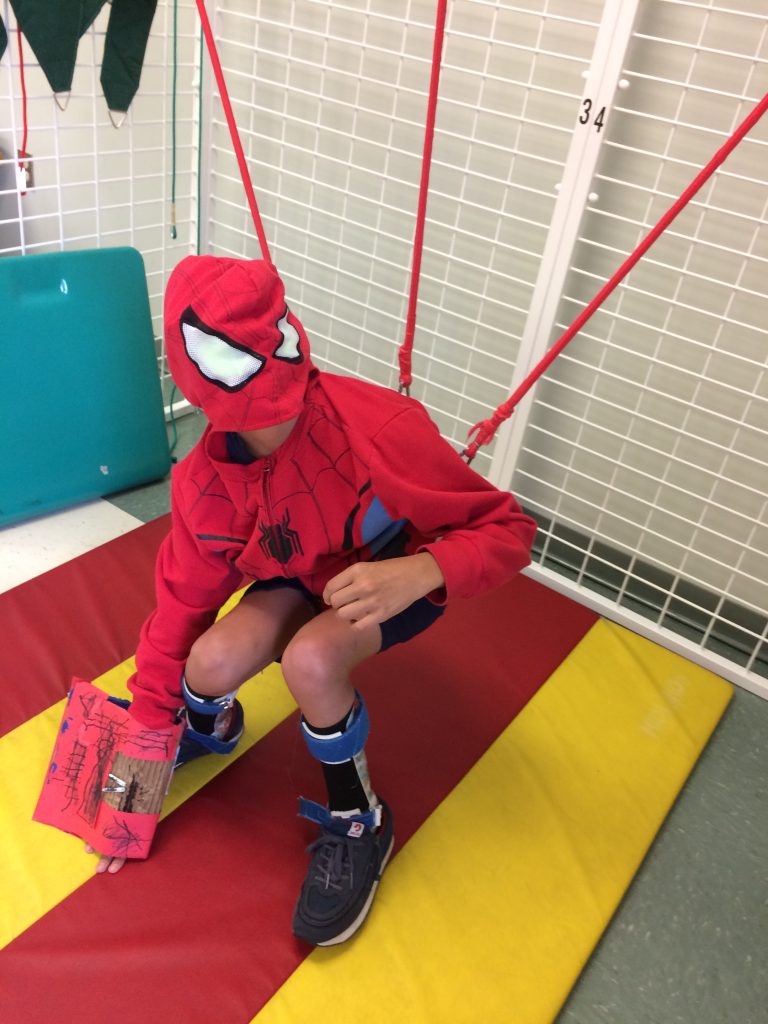

“It’s something new to torture the kids,” he said. “And by torture I mean help.”
He said it like he says a lot of things: with a mischievious smile.
His cerebral palsy makes it hard for him to walk or hold a pencil to write his name. But it has done nothing to hinder his social development.
He’s a talker, a natural storyteller with a vivid imagination and a quick sense of humor. His mom Casey Trone said Sam wants to work at Marvel Comics in New York City.
“I think he’s going to single-handedly write the next Marvel movie,” she said.
That’s the plan right now. For that to happen, there’s still a lot of work to do. Given how far he’s come, though, nobody would bet against it.
Sam was born prematurely in August 2009 and spent five months in the neonatal intensive care unit at Hershey Medical Center. Casey said she started Early Intervention services with Schreiber as soon as she received the diagnosis.
The EI services continued until he was 3. He had a muscle-lengthening surgery at age 4, which helped him make a lot of progress. A year or so later, he returned to Schreiber to resume physical therapy. Around the same time, he started school, first enrolling in Head Start when he was 4 and then starting kindergarten the next year.
“I was a little reluctant,” said Casey, who lives in the Penn Manor School District. “I would have liked to have a little more time for him to develop physically. But he did really well in kindergarten. He’s had an aide with him every year, so the support has been really good.”
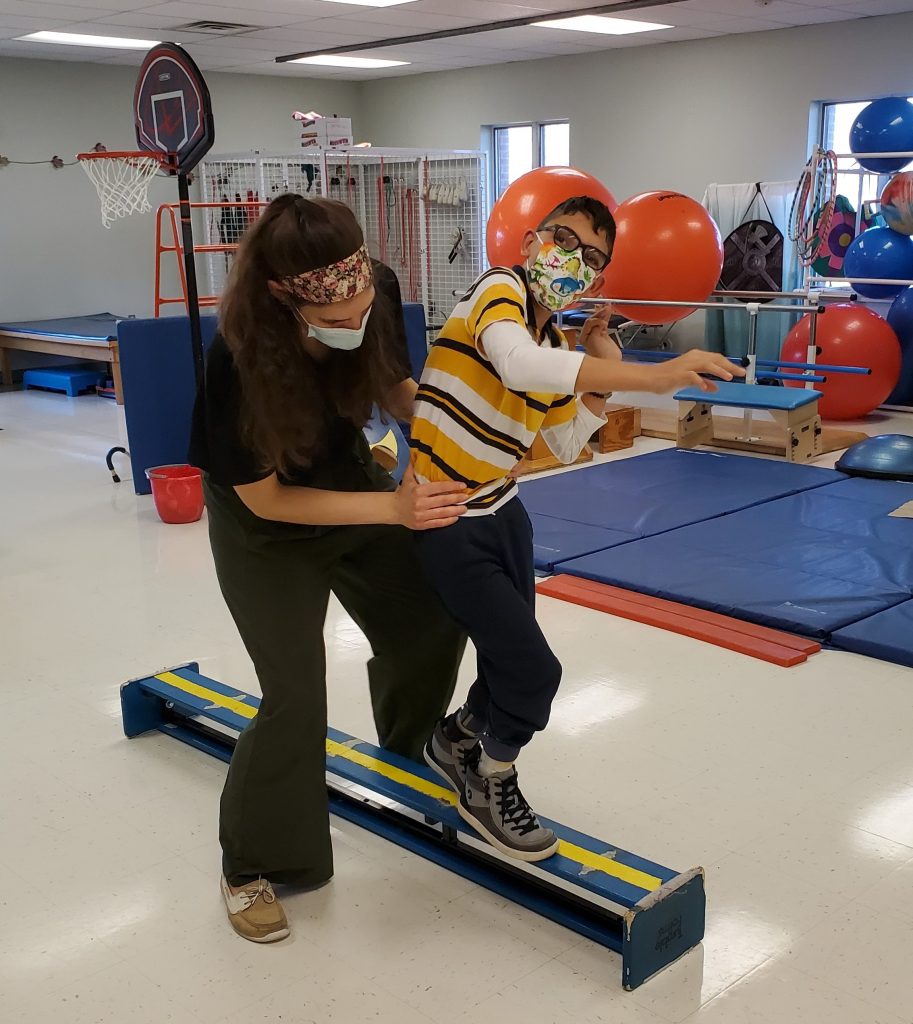

He has continued to do well in school, including his middle school years at Manor Middle School.
“He has shocked me,” Casey said. “I remember when I first got the diagnosis of CP, I had no idea what was going to happen. There are so many different forms of the disease. I went so far as to have weight-loss surgery because I didn’t know whether I was going to be able to take care of him. But he’s doing very well.”
A lot of that she attributes to their experience at Schreiber.
“It’s helped me to understand what is possible and what to do and how to take the next step with him,” she said, her voice cracking and a tear rolling down her face. “My life now is to get him to be the best he can be.”
The physical challenges haven’t been the only ones for Casey, Sam and Sam’s twin sister Isabelle. The twins’ father, Henry Leon-Rivera, passed away in 2016. Two years later, Casey brought Mike Trone into their lives.
“They were just about to turn 8,” Mike said. “When we met the first time, we went out for ice cream. We talked a lot about the ‘Cars’ movies. He’s a smaller guy, and he was even smaller then. But he can talk. He knows what he’s talking about. And he has comedic timing. He’s full of life.”
Now it was Mike’s turn to wrestle with his emotions, and he reached over to grasp Casey’s hand.
“I’ve learned so much from him,” he said finally. “I didn’t know anything about CP when Casey and I met. I guess I had a picture in my mind. And he was nothing like that. Resilience is how he approaches day-to-day life. He’s definitely changed my outlook on the world.”
And now the three-person family is four: Casey and Mike married in 2021. She’s financial coordinator with the Library System of Lancaster County. He’s a Realtor with Keller Williams Keystone. Together, they are rebuilding life as a family. And coming to Schreiber to help Sam become his best self, to fulfill his plans of telling the next stories in the Marvel universe.
“I work really hard every day to give Sam the best life I can,” she said. “And I know he meets me halfway to give his best. We all do what we gotta do, and we’ll get there.”
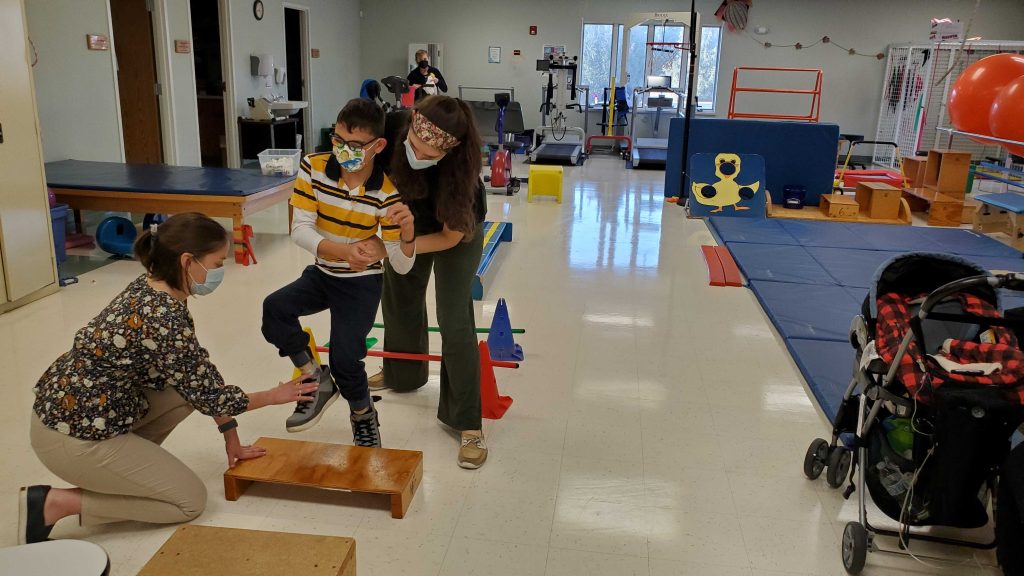

Carter Peiffer: Back from the brink
March 17, 2022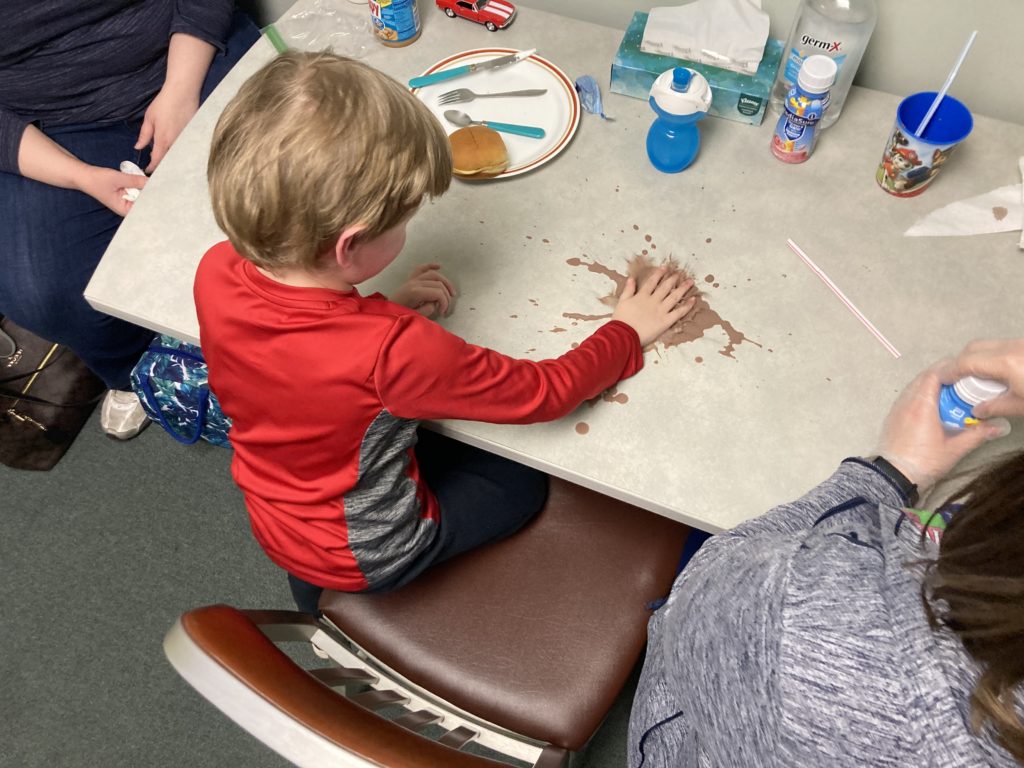
For Carter Peiffer, an occupational therapy session with Sarah Terry will usually involve food. And making a mess with food.
The mess is by design. A puddle of PediaSure on the table is fair game for Carter to write his name in, drive a toy car through or give a sip to Elmo. He might pull a straw from a cup filled with the nutrition drink and sniff (good) or take a tiny taste (better) from the end of the straw.
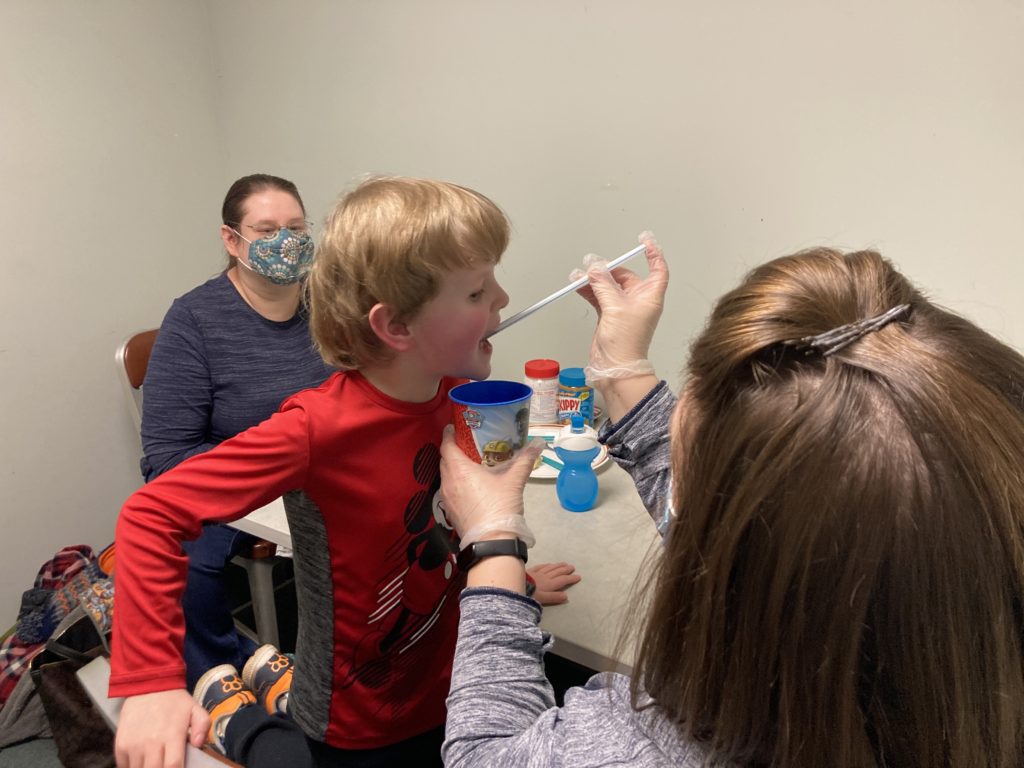
It’s all about making food fun for Carter, giving him positive experiences. He and food have had a rough two years. Through a series of life events, Carter went from a happy, active 2 year-old who would eat lots of different foods to a 4 year-old who would only eat strawberry banana yogurt — and it had to be Gerber’s. The lack of variety and nutrition in his diet over time left him with a severe vitamin C deficiency and a case of what used to be called scurvy. That caused his bones and muscles to weaken, to the point where his bones became brittle and he couldn’t walk or even stand without help.

Let’s go back to the beginning. When he was 2, his mother Desiree said she noticed Carter was a little delayed in speech. But he was otherwise active and healthy. Then he gradually began to cut out some foods, starting when Carter’s brother was born. Around the same time, his grandmother was in the hospital for an extended period following heart surgery.
These new stresses in his life caused him to become even more picky with his eating, to the point where all he would eat was the yogurt.
In March a year ago, Carter was running around playing when he tripped and fell. He ended up breaking the growth plate in his left knee, which required a knee immobilizer. A month later, he fell again — still wearing the immobilizer on his right knee — and broke the growth plate in his other knee.
After another round of medical visits, doctors at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia in May found multiple tiny fractures in his bones and sent him to CHOP’s emergency department for an immediate, intensive examination.
Their conclusion: Carter’s increasingly limited diet for more than a year had caused a dangerous vitamin C deficiency that had weakened his bones and left him susceptible to fractures. His overall medical state was as fragile as his little brittle bones.
He spent nine days at CHOP in May receiving treatment and starting inpatient therapy. Later that month, after he was sent home, Desiree called Jen Bachman, our social services director, to arrange starting services at Schreiber.
In early June, Carter had his first physical therapy visit. After not being able to put any weight on his legs because of his knee injuries, step one in his recovery was relearning how to walk. He did aquatic therapy in our therapy pool with Megan Campbell Roland, and PT in the gym with Laurie Panther.
Desiree said Laurie noticed some sensory issues and suggested Carter be evaluated for occupational therapy. In September, doctors diagnosed him with autism and sensory processing disorder, and he started working with Sarah for OT. The work there has focused on helping him expand the variety of foods he ate.
“Carter, what did you eat today?”
Sarah asked the question at the start of a recent therapy session.
“Some peanut butter bread, and I ate some hot dog!”
“You did not,” Mom said. She smiled and gave him a what-are-you-talking-about look. “You had some yogurt.”

“Yogurt,” Carter repeated back, and then swirled some PediaSure around the table with his fingers.
Sarah had a dry erase board next to her with Carter’s eating goals for the session written in blue marker. When Carter accomplished one of his tasks for the session, Sarah had him fill in the box next to that task on the white board.
The work with Sarah on eating is paying off. Desiree said Carter weighed 29 pounds when he arrived at CHOP a year ago and 32 pounds when he left. Today, his weight consistently ranges between 42 and 45 pounds.
“Sarah got him to eat peanut butter and marshmallow (sandwiches),” she said. “He started eating chips. He tried an animal cracker and a pretzel. He seems to like the crunchy stuff.”
It’s a constant process, sometimes painfully slow, sometimes with setbacks.
“When he gets derailed, when he gets sick, he shuts down (and stops eating),” she said. “I’ve had to stay up all night with him to give him water, because getting dehydrated would mean we’d have to go to the ER.”
The progress is obvious, and not just with his eating.
“He’s able to walk and run and is almost back to where he was before all this started,” Desiree said. “He plays on the playground. He goes up and down steps. He’s able to express himself more now.”
Later, she talked with a lot of emotion about what she has seen bringing him to every appointment for the past nine months.
“To see his progress has been amazing. I know (coming to Schreiber) will all end at some point, but everybody has been so amazing. They are like family here, and Carter loves being here.”
After taking two tentative tastes of a strawberry nutrition drink, Carter finishes the session with a reward: a bite of his peanut butter sandwich.
Schreiber mom: From advocate for others to advocate for son
December 17, 2021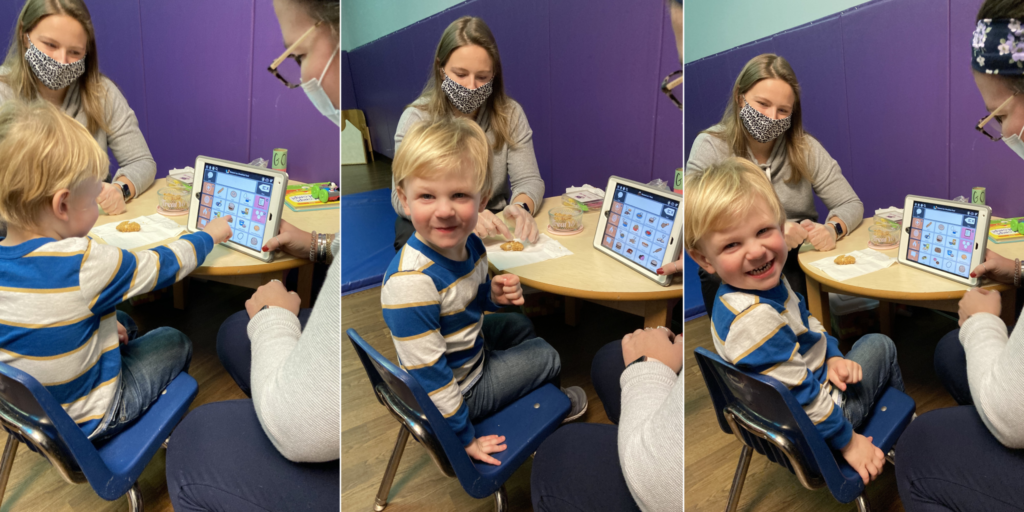
Amanda Katchur is a psychologist who has been an advocate for services that support children for a number of years. Now, she’s learning to advocate for her own child, and that’s a completely different experience.
It’s one thing to know professionally the impact that Schreiber’s services and Lancaster County’s Early Intervention program have on families. It’s another thing to see it personally.
Her daughter Bethany was diagnosed as an infant with torticollis, a condition in infants that causes a baby’s head to tilt constantly to one side. Thanks to the work of Schreiber therapists, Bethany’s torticollis is gone and she runs, jumps and dances just like any 6-year-old little girl, Amanda said.
Bethany’s little brother Leo, 3 years old, has an autism diagnosis, was born with mild hearing loss and also had some torticollis as an infant. The three issues combined have left him behind in several areas of development. When it was time for Leo to receive services through Early Intervention, at 6 months old, Amanda had no hesitation.
“I knew we wanted to come back (to Schreiber) because we had such a positive experience with Bethany,” Amanda said.
Leo has been in good hands his therapy services started. Catherine Donahue was his Schreiber’s Early Intervention specialist for home visits. Dorlas Riley was his speech-language pathologist. Denisha Roberts worked with him in physical therapy. And Bernie Hershey has been his occupational therapist.
I like to think that we’ve been fortunate to have, like, the dream team…, with all the experience they have with his issues.
AMANDA KATCHUR
“They were all really great,” Amanda said. “I like to think that we’ve been fortunate to have, like, the dream team to be quite honest with you, with all the experience they have with his issues.”
COVID has, at times, made the therapy more challenging, like when the family had to switch to telehealth services for a time. At those moments, she could see the lengths the Schreiber team would go to for a child.
When telehealth sessions switched back to in-person visits, the change and the lack of consistency caused some challenges for Leo, as it does for many kids on the autism spectrum.
“Bernie showed up at one point at our house in costume as Jessie from “Toy Story” to try to re-engage after telehealth with Leo a little bit,” Amanda said. “They just really always made an attempt (to find what) he was interested in and get into his world, which I appreciated so much.”
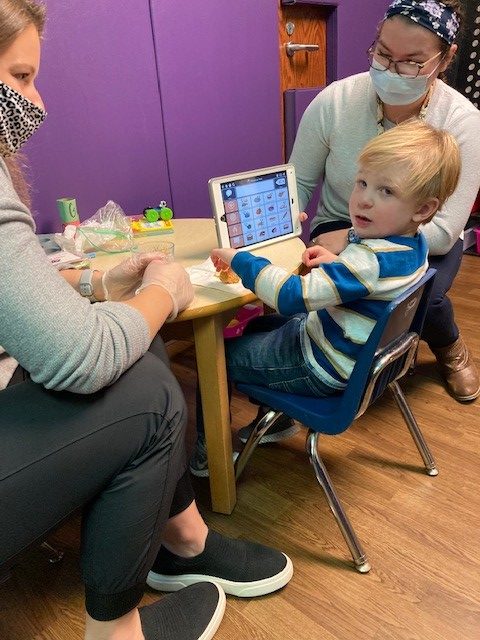
During a recent therapy session at Schreiber, Leo worked with Marli Hess, an intern in Occupational Therapy, and Maddy Sova, a speech-language pathologist. They were trying to help him become more comfortable with a different kind of food – in this case, a chicken nugget – and to improve his language skills by using a smart tablet to respond to questions.
“We are working on communication in whatever way Leo feels most comfortable,” Amanda said. “Today, you saw him working on some eating, because eating has been a struggle for us, too. So he’s been working on increasing his tolerance for different foods and different textures and things like that. But communication has been, I would say, the biggest one.”
Mom was impressed with the way Leo greeted a visitor to the session, smiling and waving. “He probably wouldn’t have done that six months ago,” she said.
EI services do make a difference

Mandy Kolb Lyons is a coordinator in Lancaster County’s Early Intervention services program. She sent this email to agencies that provide Early Intervention services after a recent presentation to the agencies by Amanda Katchur. Amanda presented at the PA Statewide Interagency Coordinating Council (SICC) meeting to share her family’s story and how Early Intervention supported them.
Here’s an excerpt from Mandy’s email:
“Amanda shared numerous examples of how you helped to coach, support, empower and guide her and her family. Amanda beamed as she shared the journey that her son and family had with Early Intervention and mentioned a few times how Early Intervention supported her entire family, including Leo’s big sister! Not only did Leo grow and progress throughout services, his entire family did. We can only hope that every family that participates in Early Intervention can walk away feeling similarly to how Amanda and her family did after participating in our services.”
First steps on a journey of recovery
December 18, 2019Four-year-old Jack Teyssier works through a series of exercises each week at Schreiber. His physical therapy sessions include strengthening and stretching for his lower left leg, some core work and some myofascial release by Schreiber therapist Lisa Stachler-Volk.
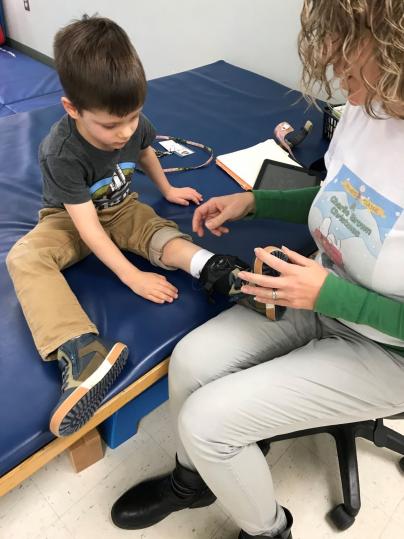
Jack Teyssier, 4, finishes his physical therapy session with Schreiber PT Lisa Stachler-Volk.
It’s hard to tell what exactly Jack is dealing with until Lisa puts some kind of black brace-like device on Jack’s left ankle.
Jack has one of the rare disorders therapists at Schreiber see from time to time. In this case, he has myofibromatosis, a condition that causes benign tumors to grow anywhere in the body.
According to the National Organization for Rare Disorders, most cases occur in young children and there can be a familial link. Jack’s mother Kara Teyssier said she had them on her leg and back; they were surgically removed when she was a baby. Her youngest son, Levi, also had one inside his cheek that was treated through chemotherapy and surgery.
It hasn’t been so simple with Jack.
“He has quite the medical history,” Kara said.
While Jack did his exercises with Lisa, Kara went through the list of Jack’s issues.
When he was born, he was diagnosed with pyloric atresia, an obstruction in the part of the stomach that leads to the small intestine. Doctors at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia repaired that through surgery, and they also found the first his benign tumors.
At one month, Kara said she and her husband, Ben, noticed Jack’s left foot was droopy. Another of these tumors had developed and was pressing on a nerve in his leg.
So Jack went through a course of chemotherapy, and Kara said most of the tumors have shrunk or disappeared. But the one in his leg had caused permanent damage to the nerve. and Jack had lost the ability to flex his foot normally.
From the time Jack was 7 or 8 months old, Schreiber therapists began working with him at home. That lasted about a year and a half, until the Teyssiers decided he was doing well enough with a brace on his left leg.
Over time, though, his doctors wanted to try and restore more flexibility in his foot. They recommended another surgery, this time to take a tendon from the bottom of his droopy left foot and move it to the top of the same foot.
That surgery happened in March 2019, and he started coming to Schreiber for physical therapy in April.
Lisa has worked on helping him walk better. Before the surgery, the brace kept his foot in a neutral position to help him walk. But he couldn’t flex his foot at all.
“The surgery helped,” Lisa said. “He couldn’t lift his foot at all when we started. Now, he can keep his foot in a neutral (not drooping) position without the brace.”
She has been working on improving the strength of his left leg; his foot tended to roll and he would walk on the side of his foot. He’s also better able to flex his foot up and down. How far he will eventually progress isn’t known.
He can run around and play just like any other 4 year old. He rides a bike without training wheels. When he walks, you can’t even tell he has any kind of a problem, Kara said.
“We have been pleased with his progress,” Kara said. “At home, he doesn’t even wear the brace a lot of the time. Long term, we don’t know if he’ll have to keep the brace. Time will tell what happens as he continues to grow and get stronger. We’re blown away with how far he’s come.”